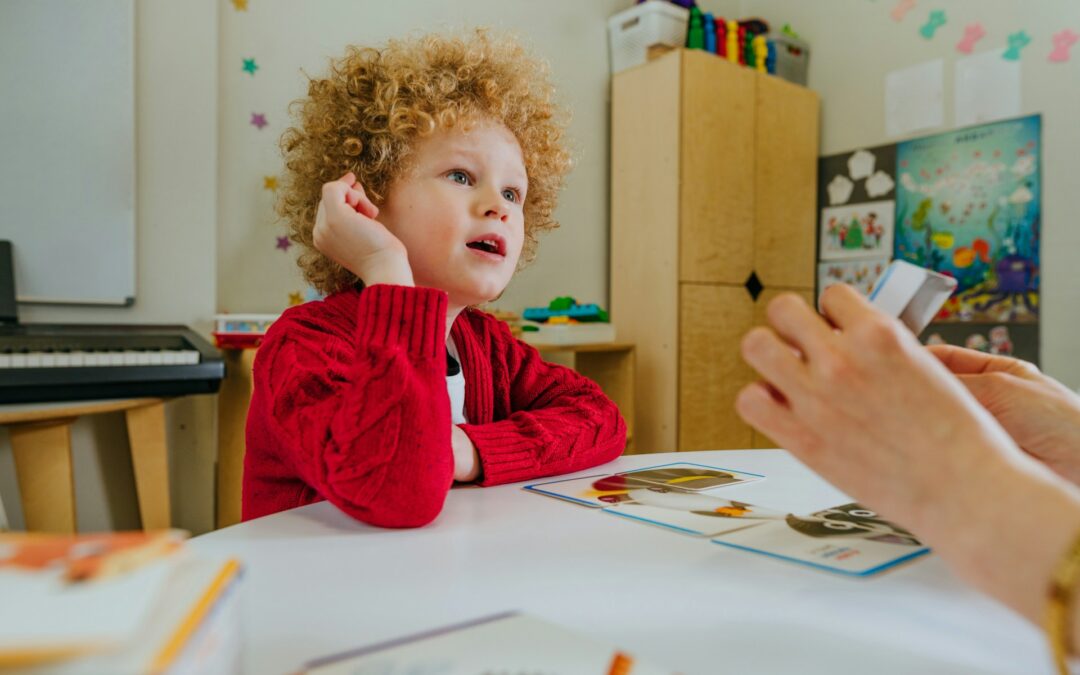
Social skills are critical components of successful everyday interactions for all individuals, and for children with autism, these skills may need to be explicitly taught and practiced. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a well-established, evidence-based approach for addressing social skill deficits in children with autism and other developmental disabilities.
By integrating social skills training within ABA therapy, Strive ABA Consultants is dedicated to helping children overcome social barriers and enhance their ability to communicate, connect, and navigate a complex world successfully.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of social skills training in ABA therapy for children with autism. We will discuss the various domains of social skills, common challenges faced by children with autism, evidence-based strategies to address these challenges, and how a personalized and comprehensive ABA therapy program can contribute to fostering better social connections and lasting success.
Domains of Social Skills: Building a Foundation for Success
Social skills encompass a broad range of abilities that are essential for successful interactions and communication with others. By addressing each of these domains in ABA therapy, we can help children with autism build a strong foundation for better social connections. Key domains of social skills include:
- Communication Skills: The ability to express oneself effectively and understand others is crucial. Verbal and non-verbal communication skills, including gestures, facial expressions, and tone of voice, all contribute to successful interactions.
- Emotional Skills: Recognizing, understanding, and managing one’s emotions, as well as empathizing with others, are vital for developing and maintaining relationships.
- Cognitive Skills: The ability to interpret social cues, perceive the intentions of others, and make appropriate decisions is critical in various social situations.
- Behavioral Skills: Adapting to different environments and situations, as well as exhibiting appropriate behaviors and manners are essential for building and maintaining social connections.
Challenges Faced by Children with Autism in Social Skills Development
Children with autism often face unique challenges when it comes to developing social skills. Some common issues include:
- Difficulty Understanding Social Cues: Children with autism may struggle to interpret facial expressions, body language, and verbal cues which can make social interactions challenging.
- Difficulty with Eye Contact: Maintaining appropriate eye contact can be a challenge for children with autism, leading to awkward or misunderstood encounters with others.
- Poor Communication Skills: Verbal and non-verbal communication deficits can make it difficult for children with autism to express their thoughts and feelings or understand others effectively.
- Difficulty with Emotional Regulation: Managing and expressing emotions appropriately is often a challenge for children with autism and can negatively impact social interactions.
Evidence-Based Strategies for Addressing Social Skill Deficits
ABA therapy employs various evidence-based strategies to address the unique social skill deficits faced by children with autism. These strategies include:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): DTT involves breaking down complex social skills into smaller, teachable steps. Each step is explicitly taught, practiced, and reinforced to help children with autism progress towards mastery.
- Social Stories: Developed by Carol Gray, social stories are narrative tools that describe specific social situations and provide guidance on appropriate behavior and responses. These stories can help children with autism better understand and navigate different social scenarios.
- Video Modeling: Researchers have found that using video models depicting appropriate social behavior can help children with autism learn and generalize social skills. This approach can be particularly beneficial for those who are visual learners.
- Peer-Mediated Instruction: Involving neurotypical peers in the social skills training process can help children with autism learn appropriate behaviors through direct interaction, observation, and imitation.
Tailoring ABA Therapy to Meet Individual Social Skill Needs
At Strive ABA Consultants, we understand that each child’s social skill needs and strengths are unique. Our experts work closely with families to develop personalized, comprehensive ABA therapy programs that prioritize and target the social skill areas most critical for each child’s success.
By implementing data-driven interventions and consistently monitoring progress, our team ensures that children receive the most effective support possible to enhance their social skills and promote better connections with others.
Building Lasting Social Connections through ABA Therapy
Investing in social skills training through ABA therapy is essential for children with autism to develop meaningful relationships, experience success in everyday interactions, and ultimately achieve a higher quality of life. At Strive ABA Consultants, our team of professionals is committed to guiding children through developing essential social skills to empower them to break through barriers, forge lasting connections, and embrace their full potential.
Final Thoughts
Social skills training in ABA therapy plays a crucial role in helping children with autism navigate the complexities of social interactions with confidence and success. By understanding the significance of social skills and employing evidence-based strategies, Strive ABA Consultants is dedicated to fostering better communication, understanding, and connections for children with autism.
Whether it’s building a foundation of communication skills, enhancing emotional regulation, or facilitating social integration, our team of professionals is here to help. Contact Strive ABA Consultants today to learn more about our social skills training services and how we can support your child’s journey toward a more socially connected and fulfilling future.