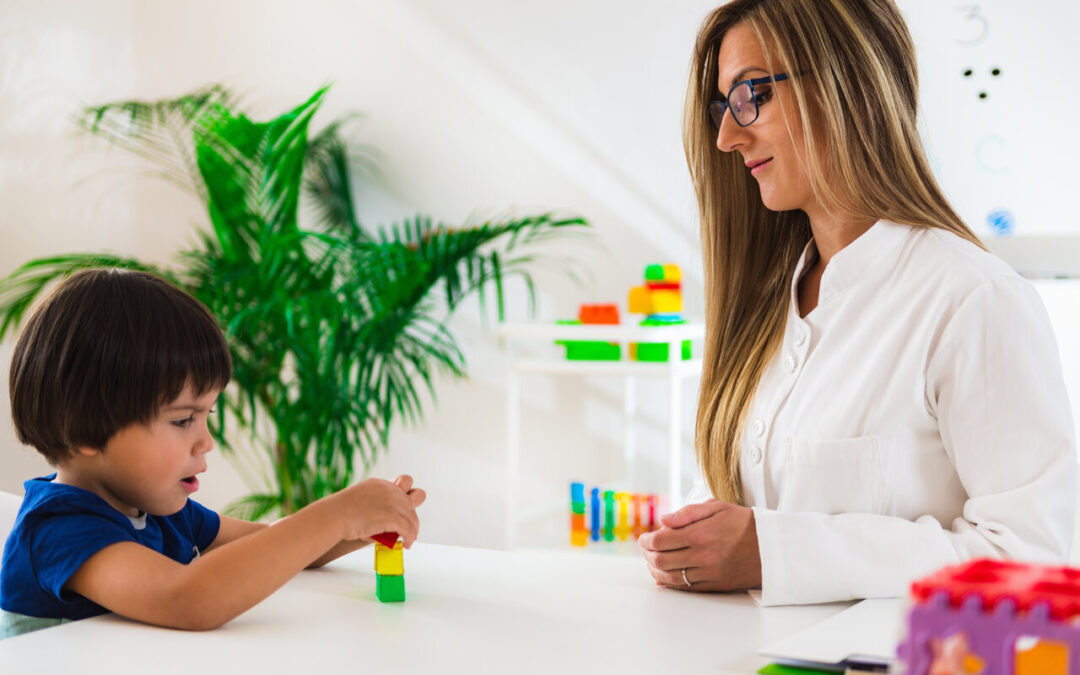
Social skills are essential elements of human interaction, enabling us to navigate personal and professional relationships, communicate effectively, and foster the connections that enhance our lives. For children with autism, however, developing these fundamental skills can be challenging, as they may not always intuitively understand social norms, cues, or interactions that many people take for granted. As a result, it’s crucial to equip children with autism and their families with the right tools and strategies to help build and improve social skills, fostering both independence and inclusion.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a powerful and evidence-based intervention that has shown efficacy in promoting social skills development in children with autism. Leveraging proven strategies and techniques, ABA therapy focuses on breaking down complex social interactions into smaller, more manageable components, allowing children to learn, practice, and master these essential skills over time. ABA therapists employ a range of approaches, such as role-playing, reinforcement, and video modeling, to facilitate meaningful and targeted learning experiences that improve the social abilities of children with autism.
Whether you are a parent, educator, or professional working with children with autism, join us as we delve into the world of ABA therapy and social skills development, unveiling its impact in transforming the lives of individuals with autism and their families.
Common Social Skill Challenges in Autism
Children with autism often face a range of social skill challenges that can hinder their ability to form connections, communicate effectively, and participate fully in everyday activities. These challenges can vary significantly depending on the individual but may include the following:
- Difficulty reading social cues: Children with autism may struggle to decode nonverbal communication cues such as facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice, which can adversely affect their understanding of social situations.
- Limited eye contact: Engaging in eye contact can be uncomfortable or challenging for children with autism, making it difficult for them to convey attention or interest in social interactions effectively.
- Difficulty initiating and maintaining conversations: Navigating conversations can be especially complex for children with autism, as they may struggle with expressing their own thoughts, making conversational turns, or interpreting the thoughts and feelings of others.
- Challenges with emotional regulation: Children with autism may experience heightened emotional responses and have difficulty managing their emotions in social situations, which can be perceived as overreacting or poor coping skills.
ABA Strategies for Targeted Social Skills Development
To address the varied social skill challenges faced by children with autism, ABA therapists employ a range of strategies and techniques designed to promote meaningful progress in targeted areas of social functioning. Some of these strategies include the following:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): This structured teaching approach involves breaking down specific social skills into smaller, more manageable components, enabling children to practice and master each part before combining them into more complex behaviors.
- Natural Environment Teaching (NET): In this form of teaching, ABA therapists encourage the development of social skills by embedding learning opportunities within naturally occurring activities, allowing children to practice and generalize their social skills within their everyday environment.
- Role-Playing: Role-playing exercises provide children with autism a safe and supportive space to practice new social skills, experiment with different behavioral responses, and receive feedback and guidance from therapists and caregivers.
- Social Skill Groups: ABA therapists may run or facilitate social skills groups where children with autism can engage in structured, interactive activities with peers, allowing for skill practice and development in a group setting.
Examples of Targeted ABA Interventions for Social Skills Development
ABA therapy offers the flexibility to customize interventions based on the individual needs and goals of each child with autism. Some examples of targeted ABA interventions designed to foster growth in social skills development include the following:
- Using DTT to teach turn-taking: ABA therapists may utilize Discrete Trial Training to break down the steps of turn-taking in games or conversations, offering reinforcement and repetition until the child demonstrates mastery.
- Utilizing NET to enhance reciprocal communication: Natural Environment Teaching can be employed to teach children skills such as initiating conversations, asking and answering questions, and maintaining conversational topics within the context of their daily routines.
- Role-playing for practicing emotional regulation: ABA therapists may develop role-playing scenarios that challenge children to identify emotions, express their feelings appropriately, and develop coping strategies to regulate their emotions in various social situations.
- Facilitating social skill groups for practicing joint attention: Collaborative play or group activities designed by ABA therapists can encourage children with autism to practice joint attention, an essential skill for navigating group dynamics and forming connections with peers.
The Impact of ABA Therapy on Social Skills Development
When implemented effectively, ABA therapy can have a transformative impact on the social skills development of children with autism. Through evidence-based strategies and targeted interventions, children can achieve the following:
- Enhanced communication and interpersonal skills: Children with autism can experience improvements in their ability to engage in reciprocal conversations, interpret non-verbal cues, and maintain eye contact.
- Improved emotional regulation: ABA therapy can support children in learning to identify their emotions and effectively utilize coping strategies, fostering increased resilience and adaptability in social situations.
- Increased opportunities for social inclusion: As children with autism develop their social skills, they may experience greater opportunities for inclusion in community activities, recreational programs, and educational settings.
Conclusion
Fostering the development of social skills in children with autism is an essential aspect of maximizing their potential and enhancing their quality of life. Through targeted ABA therapy interventions, Strive ABA Consultants is committed to supporting children with autism in overcoming social skill challenges, paving the way for increased independence, meaningful relationships, and a world of opportunities.
If you’re looking for effective autism treatment strategies to enhance your child’s social skills development, get in touch with Strive ABA Consultants today. Our team of experts can provide evidence-based methods that have been proven to transform the lives of children with autism.