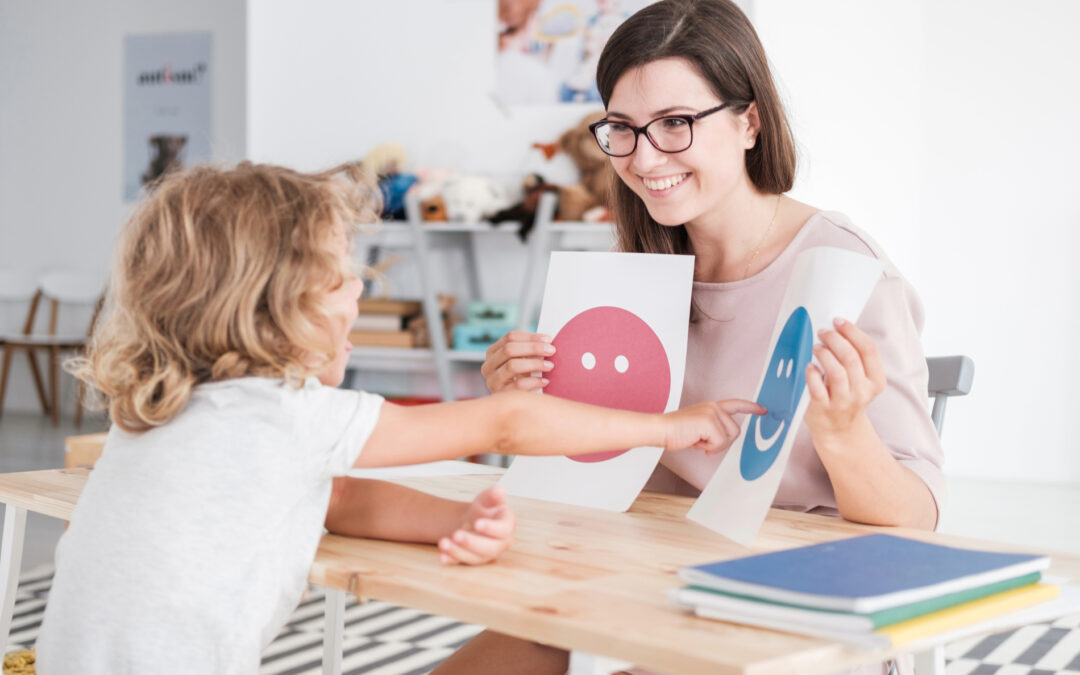
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a well-known approach for helping individuals with autism and other developmental challenges. It focuses on teaching new skills and reducing behaviors that can interfere with learning and daily life. The techniques used in ABA are based on research and have a strong track record of success.
ABA therapy is unique because it is customized to the needs of each person. This means that goals are set based on the individual’s strengths and challenges. Therapists use these goals to create an effective plan to teach important skills and improve behavior, making everyday life easier.
Parents and caregivers often wonder how ABA therapy works and how it can help their child. Although it involves many techniques, it is mainly about understanding why behaviors happen and how to encourage positive changes in behavior. So, we’ll shed light on what ABA therapy involves, and how it measures success, and address some misunderstandings about this approach.
The Basics of ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a scientific approach that uses techniques to bring about meaningful changes in a child’s behavior. It is particularly effective for children with autism, helping them learn new skills and improve their social interactions.
The main goal of ABA therapy is to increase positive behaviors and decrease behaviors that interfere with learning. By focusing on individual needs, ABA therapy can be tailored to fit each child’s unique learning style and abilities.
At the heart of ABA therapy is the use of reinforcement to encourage positive behaviors. This might include giving praise, tokens, or small rewards when children demonstrate desired behaviors.
Over time, these positive reinforcements help shape behavior, making it more consistent and reliable. ABA therapists work closely with children to identify which reinforcements work best.
Another important aspect of ABA is task analysis. This involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps. By tackling these smaller steps one at a time, children can better learn and master new skills. This method also helps reduce frustration and builds confidence as children achieve each step successfully.
Overall, ABA therapy is flexible and can be applied in many settings such as at home, in school, or in a clinic. It is data-driven, meaning that therapists track a child’s progress and make adjustments to the program as needed. This ensures that each child receives the most effective therapy possible.
Key Components of ABA Programs
ABA programs are built around several key components that ensure successful outcomes. Understanding these elements helps families and therapists create effective and personalized treatment plans. Here are some of the main components:
1. Individualized Assessment: Before starting ABA therapy, a detailed assessment of the child’s skills and behaviors is conducted. This assessment identifies strengths, challenges, and the best areas to target for improvement.
2. Targeted Goals: Based on the assessment, specific and measurable goals are set. These goals focus on increasing skills in communication, social interaction, and daily living, as well as reducing challenging behaviors.
3. Structured Environment: ABA programs often involve creating structured environments where children can learn. This means minimizing distractions and setting clear expectations to help children focus on their learning goals.
4. Consistent Routines: By establishing consistent routines, children understand what is expected of them. This consistency helps in reinforcing desired behaviors and makes it easier for children to learn and apply new skills.
5. Regular Monitoring and Adjustments: Progress in ABA is closely monitored. Data is regularly collected and analyzed to see how well the child is meeting their goals. If needed, programs are adjusted to ensure continued growth and success.
Using these components, ABA programs are designed to be comprehensive and adaptable, supporting each child’s unique journey in learning and development.
Measuring Progress and Success
In ABA therapy, measuring progress and success is a critical part of the process. Accurate measurement helps determine how effectively each child is learning and which aspects of the program may need adjustment.
To achieve this, data collection plays a major role. Therapists consistently track and record specific behaviors and skills over time. This data helps identify patterns and assess whether the child is meeting their targeted goals.
One common method is using baseline measurements. A baseline is the initial level of a behavior before any intervention begins. By comparing this to later data, therapists can see exactly how much progress has been made. This objective approach ensures that changes in behavior are clear and quantifiable.
Regular reviews and updates are also essential. Therapists frequently review the collected data with parents and caregivers to discuss progress. They can determine if the current strategies are effective or if modifications are necessary. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone involved understands the child’s progress and shares in the planning process.
Accurate measurement not only celebrates a child’s achievements but also empowers families and therapists to make informed decisions. This lays a foundation for continued growth and development, tailored to each child’s unique path.
Common Misconceptions About ABA Therapy
Despite its success, ABA therapy often faces misunderstandings and myths. Clearing up these misconceptions can help families make informed decisions about whether ABA is right for their child.
One misconception is that ABA uses punishment to change behavior. In reality, ABA focuses on positive reinforcement. It encourages desirable behaviors through rewards, making the therapy a positive experience for the child.
Another myth is that ABA only works for young children with autism. While early intervention is beneficial, ABA can be effective for individuals of all ages. It adapts to each person’s developmental level and specific needs, offering support throughout varying stages of life.
Some believe that ABA is rigid and doesn’t allow children to be creative or expressive. However, ABA programs are highly customizable. They are designed to build upon a child’s natural interests and talents, which can include creative activities. This flexibility helps children develop in ways that are meaningful to them.
Understanding these misconceptions helps families see the true potential of ABA therapy. It is a collaborative and positive approach, supporting children in achieving their fullest potential in a way that respects their individuality.
Conclusion
ABA therapy offers a structured yet adaptable approach to support children with autism and other developmental challenges. By breaking down skills and building upon strengths, ABA helps children achieve significant improvements in communication, behavior, and everyday skills. Each child’s journey is unique, and ABA provides the tools and strategies to support this growth.
A key strength of ABA therapy is its emphasis on data-driven practice. This ensures that the therapy remains effective and responsive to a child’s changing needs. With the right support, children gain confidence and learn to navigate their world more independently.
Strive ABA Consultants is dedicated to using evidence-based ABA therapy in Chicago to help children reach their potential. If you want to know more about how our programs can make a difference in your child’s life, contact Strive ABA Consultants today.
Let’s work together to create a brighter future for your child!