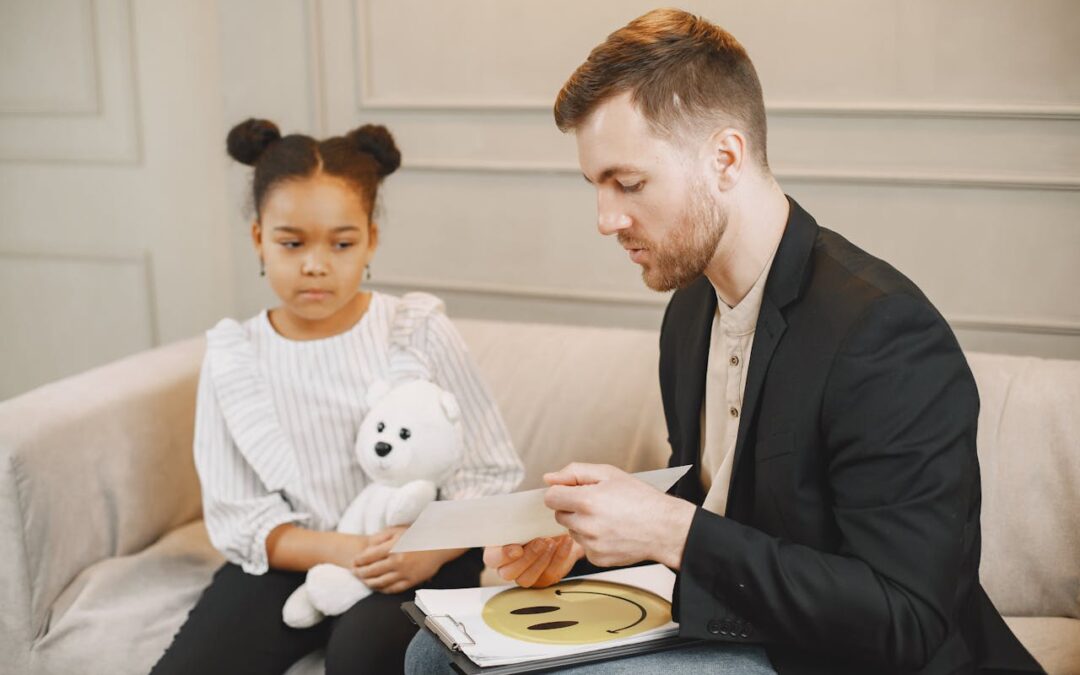
Positive reinforcement is a key element in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. This approach uses rewards to encourage good behaviors and help children with autism learn new skills. By focusing on positive outcomes, children are more likely to repeat desired actions. This makes learning more enjoyable and effective.
The idea behind positive reinforcement is simple: when a child does something good, they receive a reward. This could be praise, a small treat, or extra playtime. These rewards motivate the child to repeat the behavior in the future. Over time, positive reinforcement helps build lasting habits and boosts a child’s confidence.
ABA therapy uses positive reinforcement to teach a wide range of skills. These can include communication, social interactions, and everyday tasks. Understanding the importance of positive reinforcement in ABA can shed light on why it’s such a powerful tool in helping children achieve their full potential.
Understanding Positive Reinforcement in ABA
Positive reinforcement is a key component of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), a method used to teach new skills to children with autism. This technique involves adding something positive immediately after a desired behavior occurs, which increases the likelihood of the behavior repeating in the future. Reinforcement can take many forms, such as verbal praise, small rewards, or extra playtime. Each child may respond differently to various types of reinforcement, so it is important to find what works best for them.
In ABA, therapists carefully observe and record behaviors to determine which types of reinforcement are most effective. This helps create a customized plan tailored to each child’s needs. The goal is to reinforce behaviors that contribute to the child’s development, such as making eye contact, following instructions, or using words to communicate. By consistently applying positive reinforcement, children begin to understand the connection between their actions and the rewards they receive.
Positive reinforcement also involves setting clear expectations and goals. Children need to know what is expected of them to earn reinforcement. For example, if a child is learning to ask for help, a therapist might reinforce this behavior by immediately acknowledging their request and offering assistance along with a reward. This clear cause-and-effect relationship helps the child learn more efficiently and enjoyably.
Benefits of Positive Reinforcement for Children with Autism
Positive reinforcement offers numerous benefits for children with autism. It helps them learn new skills and improve existing ones. Since many children with autism face challenges in communication and social interaction, positive reinforcement provides a structured way to address these areas. By using reinforcement, therapists can teach children important skills that make daily life easier and more fulfilling.
One notable benefit is the boost in self-esteem that positive reinforcement provides. Children feel proud and motivated when they receive recognition for their accomplishments. This encouragement can lead to increased confidence, making them more willing to try new tasks and face challenges.
Positive reinforcement also promotes better relationships with others. When children learn skills like taking turns or sharing, they can interact more positively with peers and adults. This can lead to more meaningful friendships and improved social skills.
There are several key benefits of positive reinforcement for children with autism:
1. Increased Motivation: Reinforcement encourages children to engage in desired behaviors by providing something they enjoy.
2. Skill Development: It helps children learn and master essential life skills, such as communication and self-care.
3. Enhanced Focus: Children learn to concentrate better on tasks when they receive clear, immediate feedback.
4. Better Behavior: Positive reinforcement helps reduce challenging behaviors by focusing on and promoting positive actions.
Through positive reinforcement, children with autism can achieve greater independence and confidence in themselves. The consistent encouragement and rewards create a positive learning environment that makes it easier for them to grow and thrive.
Effective Strategies for Implementing Positive Reinforcement
Implementing positive reinforcement effectively requires planning and consistency. One important strategy is to ensure that the reinforcement matches the child’s preferences. Understanding what motivates each child is crucial in making positive reinforcement work. Some children may respond well to verbal praise, while others might be motivated by small toys or extra playtime.
Timing is another critical factor. Reinforcement should immediately follow the desired behavior. This helps the child make a clear connection between their actions and the reward. The sooner a child receives reinforcement, the stronger the learning process becomes.
Consistency is also key in positive reinforcement. Reinforcing the target behavior every time it occurs solidifies the behavior as a regular part of the child’s routine. Over time, less reinforcement might be needed, but initially, frequent reinforcement is vital.
Here’s a quick checklist for effective implementation:
1. Identify Motivators: Know what excites the child and tailor rewards accordingly.
2. Immediate Delivery: Provide reinforcement right after the behavior.
3. Be Consistent: Reinforce every occurrence of the behavior.
4. Vary Rewards: Keep rewards fresh to maintain interest.
5. Adjust Over Time: Gradually lessen reinforcement as the behavior becomes stable.
Through careful planning and application, these strategies can make positive reinforcement a powerful tool in the ABA toolkit.
Common Misconceptions About Positive Reinforcement in ABA
Despite its effectiveness, some misconceptions surround positive reinforcement in ABA. A common belief is that positive reinforcement is the same as bribery. This misunderstanding arises because both involve rewards, but they serve different purposes. Bribery is often used to stop a problem behavior temporarily, while positive reinforcement aims to build positive behaviors over the long term.
Another misconception is that positive reinforcement leads to dependence on rewards. In reality, when implemented correctly, reinforcement helps establish behaviors which later become self-reinforcing. Over time, the need for external rewards decreases as the child begins to find satisfaction in the actions themselves.
Some people think that only tangible rewards work in reinforcement. However, intangible reinforcements, such as praise and attention, can be very effective too. These social reinforcers help build a child’s self-esteem and promote continued positive behavior.
There is also a belief that positive reinforcement works only in structured settings. In truth, positive reinforcement can be applied in everyday interactions and situations, reinforcing its practicality and versatility.
Addressing these misconceptions helps clarify the true benefits of positive reinforcement and its role in nurturing growth and learning.
Conclusion
Positive reinforcement stands out as a fundamental technique in ABA therapy. It emphasizes focusing on the strengths and abilities of children, encouraging them to repeat positive behaviors by offering suitable rewards. This approach not only aids in developing essential skills but also boosts a child’s confidence, motivation, and willingness to engage in the learning process.
As we’ve seen, positive reinforcement can transform a child’s ability to interact with their environment. By using consistent and immediate rewards, therapists guide children in learning and mastering new behaviors. The effectiveness of positive reinforcement lies in its adaptability and its ability to suit individual needs, making it a versatile tool in helping children reach their potential.
For families and therapists working with children with autism, understanding and correctly implementing positive reinforcement can make a world of difference. This method fosters a supportive environment where children feel valued and encouraged to grow at their own pace and abilities.
Are you ready to explore how ABA and positive reinforcement can significantly impact your child’s development? Contact our autism center in Chicago to learn how our personalized programs can make a difference in your child’s life. Let us support you and your family in unlocking the full potential of your child through proven and effective methods. Get in touch with Strive ABA Consultants today.